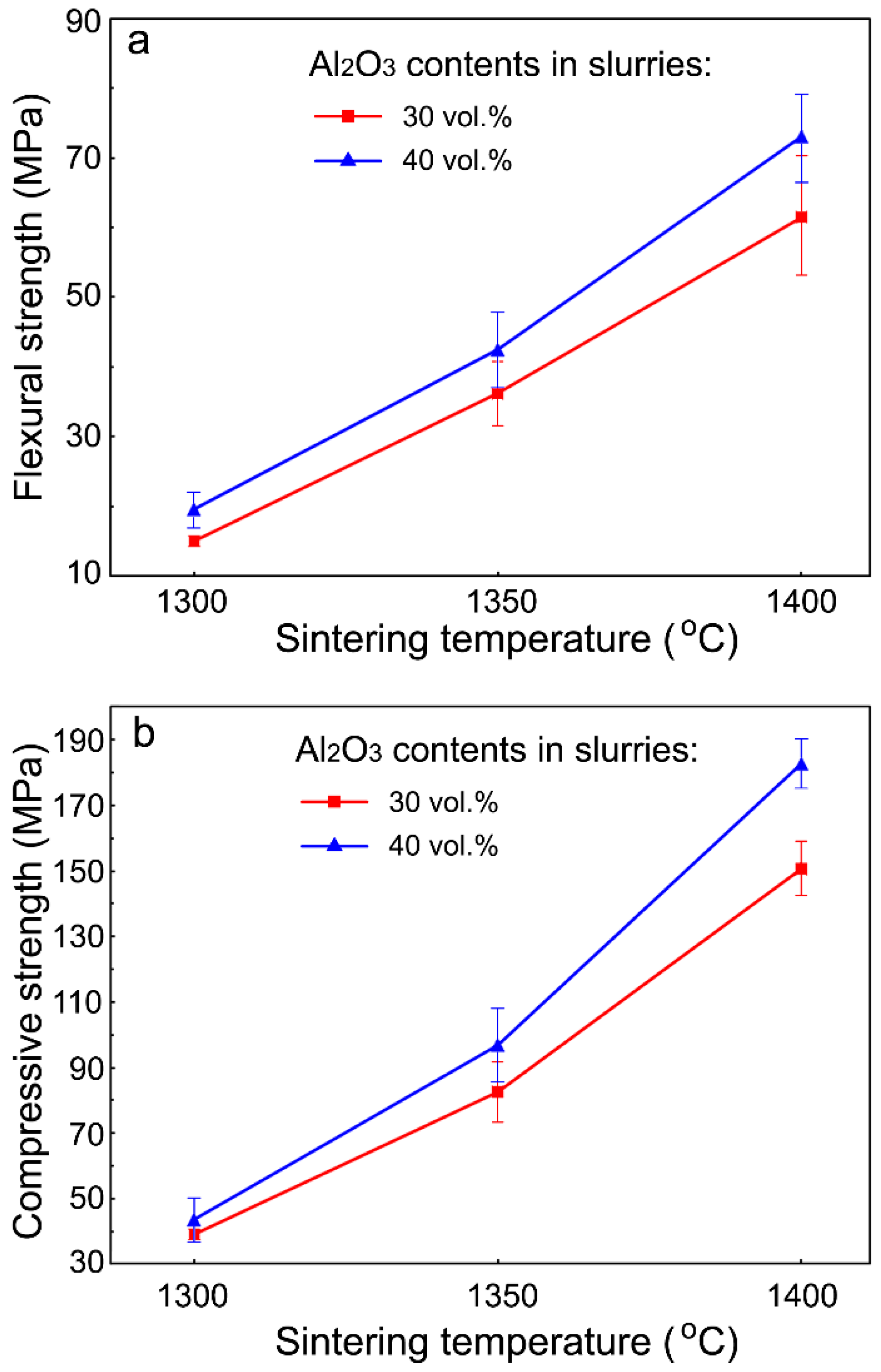
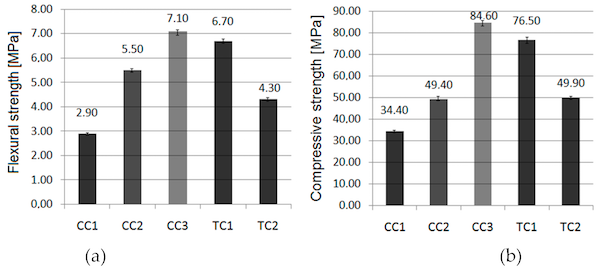
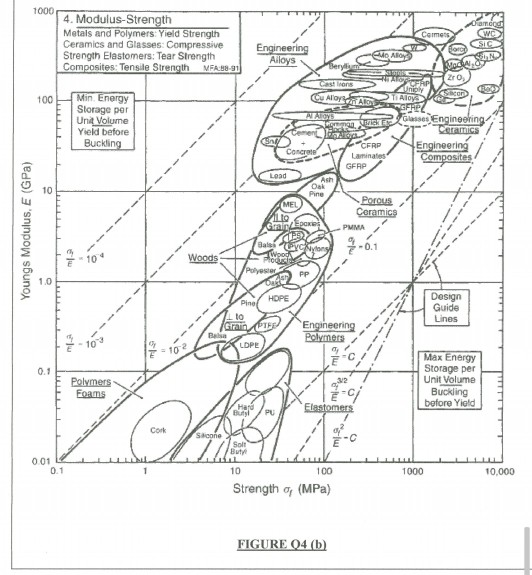
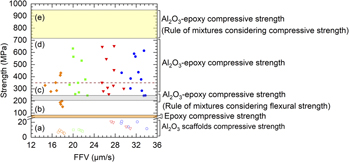
Compressive Strength Of Ceramic Materials

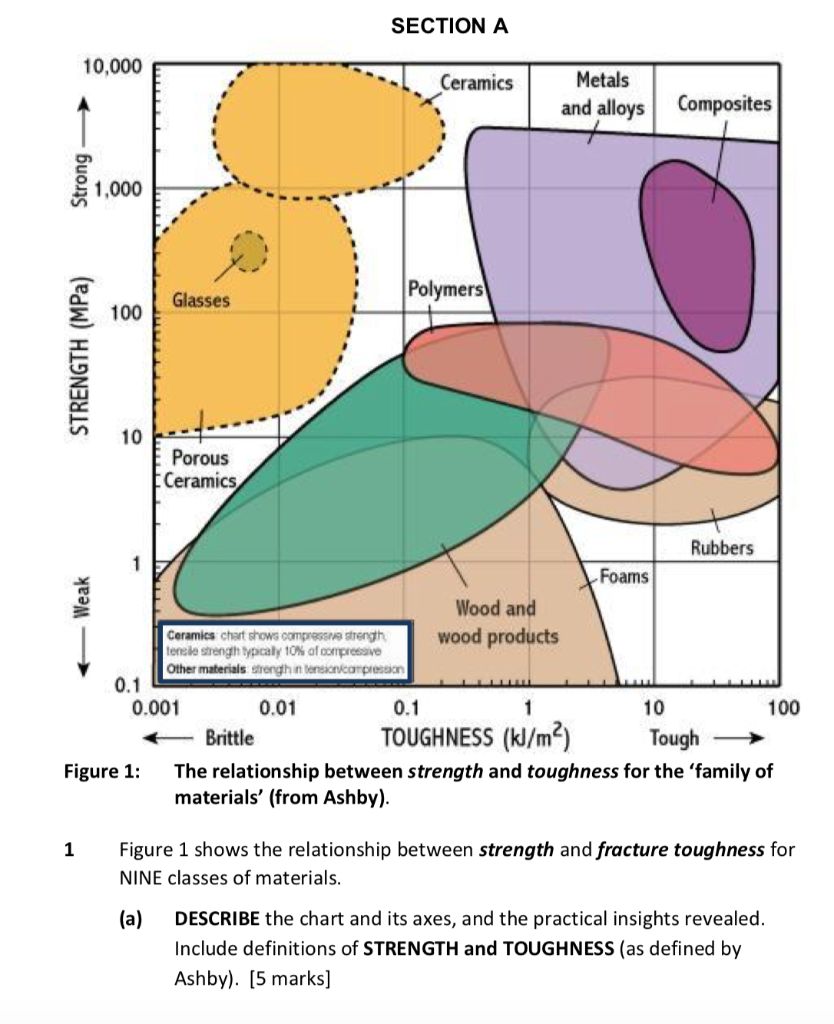
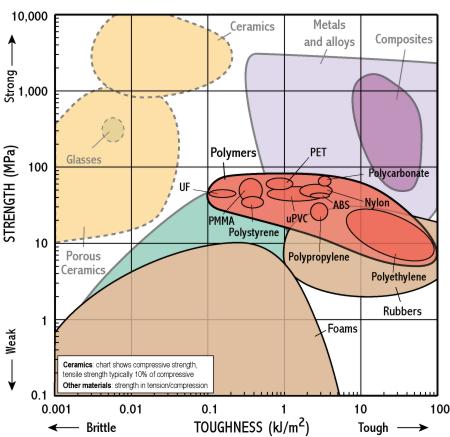
The ionic and covalent bonds of ceramics are responsible for many unique properties of these materials such as high hardness high melting points low thermal expansion and good chemical resistance but also for some undesirable characteristics foremost being brittleness which leads to fractures unless the material is toughened by.
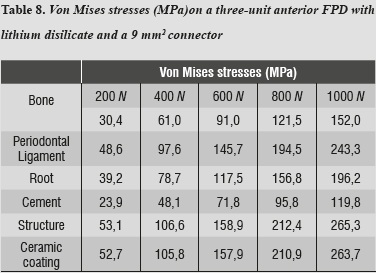
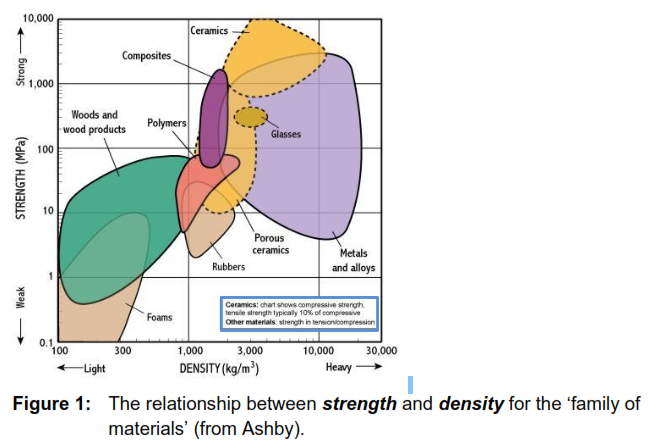
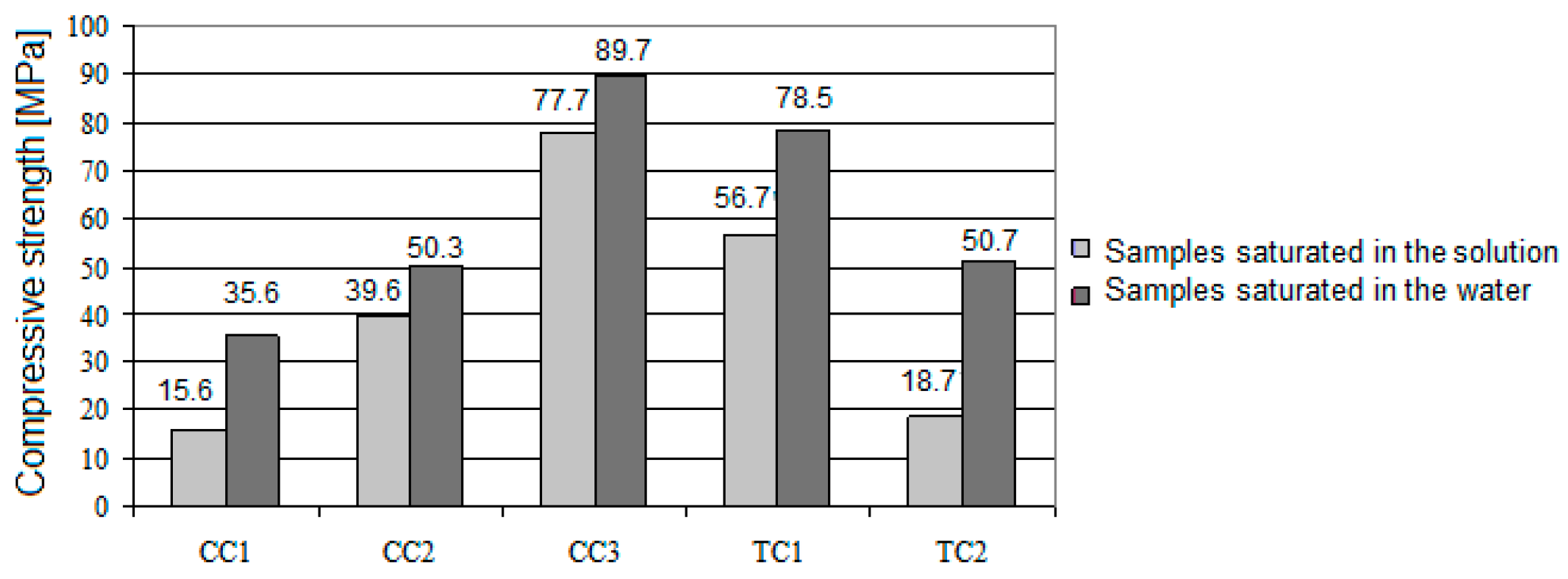
Compressive strength of ceramic materials. Material specific gravity sg coefficient of linear expansion α. Generally speaking rock bricks concrete glass and ceramics have high compressive strength. Compressive strength and durability properties of ceramic wastes based concrete. The mechanical strength was primarily influenced by the crystallinity of glass ceramics and the interfaces between the crystalline phases and the glassy matrix.
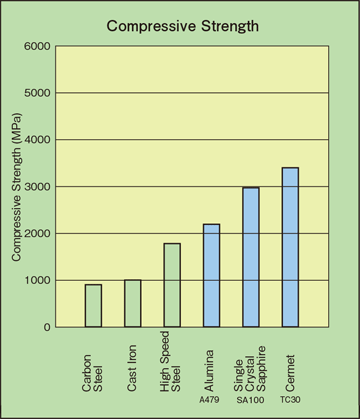
For full table with tesnsile strength compressive strength flexural strength and modulus of elasticity rotate the screen. The tensile strength measured for the material indicates that the ratio of compressive strength to tensile strength is 18. Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating selected and refined materials often including clay in the form of kaolinite to high temperatures. For a metal the compressive strength is near that of the tensile strength while for a ceramic the compressive strength may be 10 times the tensile strength.
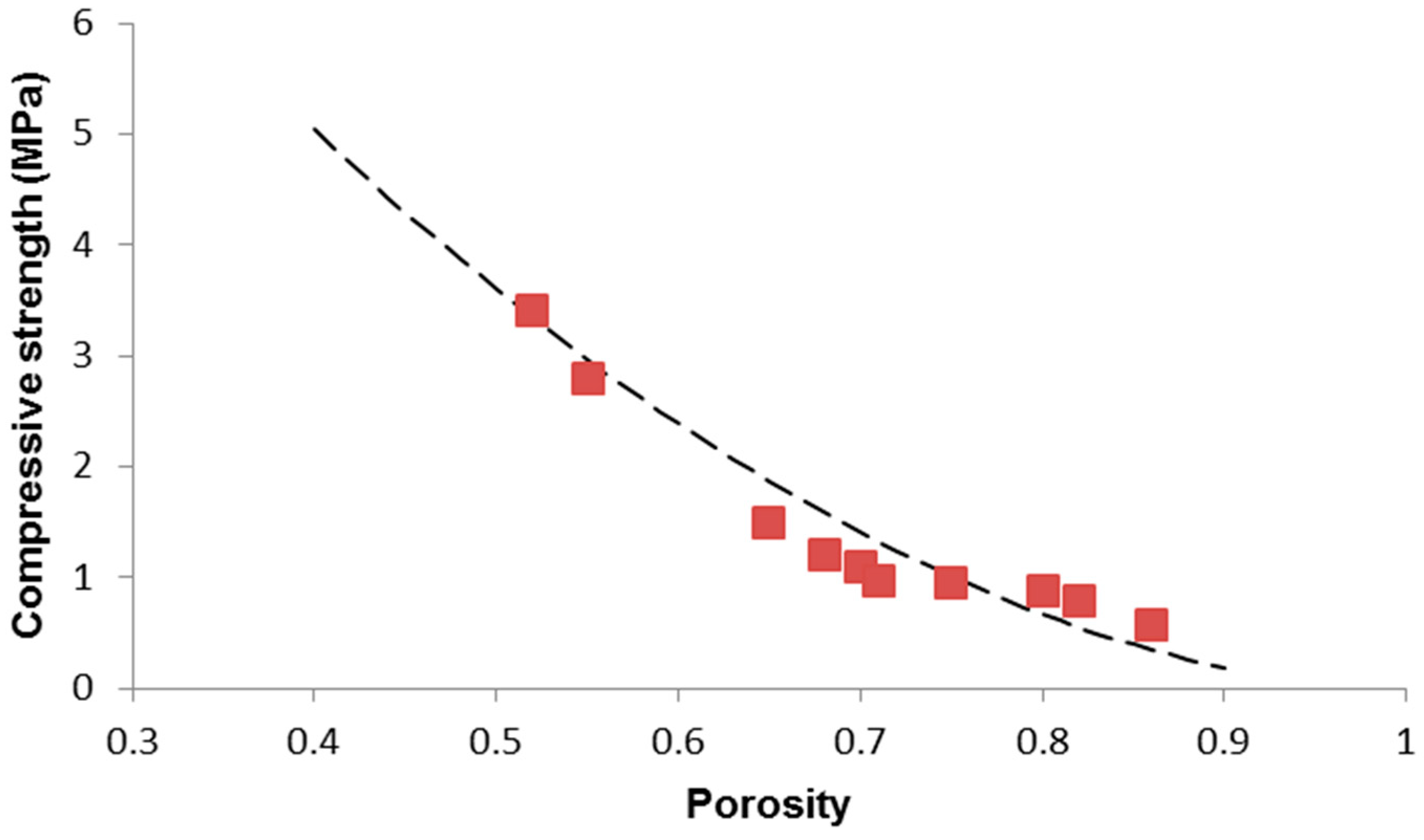
The compressive strength of porous glass ceramics firstly increased and then decreased with the sintering temperature reaching a maximal value of 1 8 mpa at 750 c. Compressive strength compressive strength is the capacity of a material to resist forces pushing it together before being compressed crushed or breaking. Compressive strength or compression strength is the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to reduce size as opposed to which withstands loads tending to elongate. The average value of the compressive strengths measured in all stress states excluding the equibiaxial and the near uniaxial compressive stress states was 528 ksi.
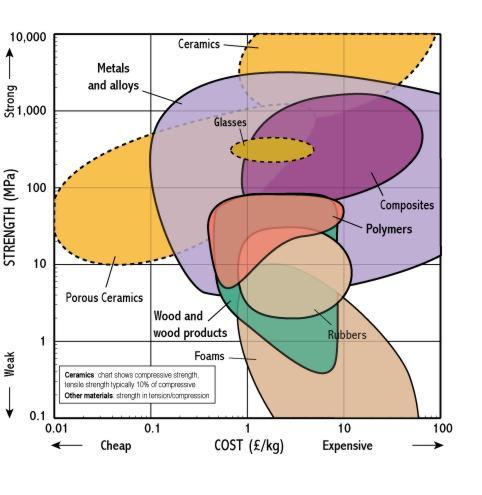
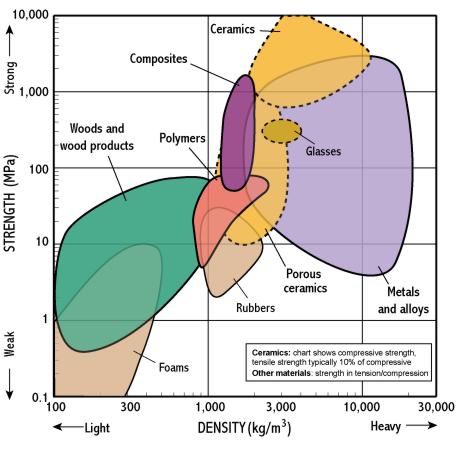
In other words compressive strength resists being pushed together whereas tensile strength resists tension being pulled apart. For example the total weight you can put on top of a concrete block before it begins to crumble. Ceramics tend to be weak in tension but strong in compression. Alumina for example has a tensile strength of 20 000 psi 1138 mpa while the compressive strength is 350 000 psi 2400 mpa.
Ceramic materials offer a number of benefits in a variety of applications. The first one are all fired wastes generated by the structural. They provide high wear heat and corrosion resistance as well as high tensile strength volume resistivity dielectric strength and modulus of elasticity.